System Architecture
Architecture Overview
FirmwareCI uses a distributed architecture with three main components: the FirmwareCI Server, Devices-under-Test (DUTs), and Clients. The server coordinates all testing activities, managing hardware resources and executing workflows triggered by clients.
FirmwareCI Server
The FirmwareCI Server is the central coordinator managing the entire testing lifecycle.
Core Functions
Job Scheduling: Queues and schedules test jobs based on workflow triggers.
DUT Management: Tracks available hardware, handles reservations, and ensures DUTs are properly configured. Integrates with external reservation systems when configured.
Test Execution: Runs test workflows in isolated containers. Manages pre-stage, test stages, and post-stage operations. Handles timeouts, failures, and cleanup.
Artifact Storage: Stores test artifacts, firmware binaries, and logs. Provides access to historical test results and reports.
Configuration Storage
The server stores all project configurations:
- Workflows: Define which tests run for which events
- DUT definitions: Hardware specifications and connection details
- Test files: Test stages and steps
- Storage items: Firmware binaries, tools, and test data
- Secrets: API tokens and sensitive configuration
Devices Under Test (DUTs)
DUTs are hardware devices connected through control interfaces that enable remote management and testing.
Interface Capabilities
Control interfaces (typically single-board computers like Raspberry Pi) provide:
- Power Control: Turn devices on/off, perform hard resets
- Serial Access: Monitor boot logs, access console
- Flash Operations: Read and write firmware to flash chips
- Binary Execution: Deploy and run test binaries
- Network Access: SSH connectivity for command execution
DUT Configuration
Each DUT has a configuration defining:
Attributes: Key-value pairs for device-specific data (hostnames, addresses, credentials).
Label: Groups DUTs of the same hardware type. Workflows target labels, not individual DUTs.
Pre-stage: Optional setup steps run before tests (flash firmware, configure BIOS).
Post-stage: Optional cleanup steps run after tests (power off, reset settings).
Reservation System: Optional integration with external hardware reservation systems.
Hardware Control
FirmwareCI delegates low-level device management to control interfaces. While design is flexible, FirmwareCI is intended to integrate with DUT‑Control (dutctl), an open‑source CLI for remote hardware interaction: DUT‑Control (dutctl). The dutctl command provides the standardized operations FirmwareCI relies on — power control, flashing, serial console access, resets.
Clients
Clients interact with the FirmwareCI Server to trigger workflows, monitor progress, and retrieve results.
Client Types
- CI System Integrations: GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and other CI platforms trigger workflows automatically on commits, pull requests, and releases.
- Web Interface: Browser UI for monitoring runs, viewing reports, and managing configurations.
- CLI Tool (fwci): Command-line tool for setup and configuration.
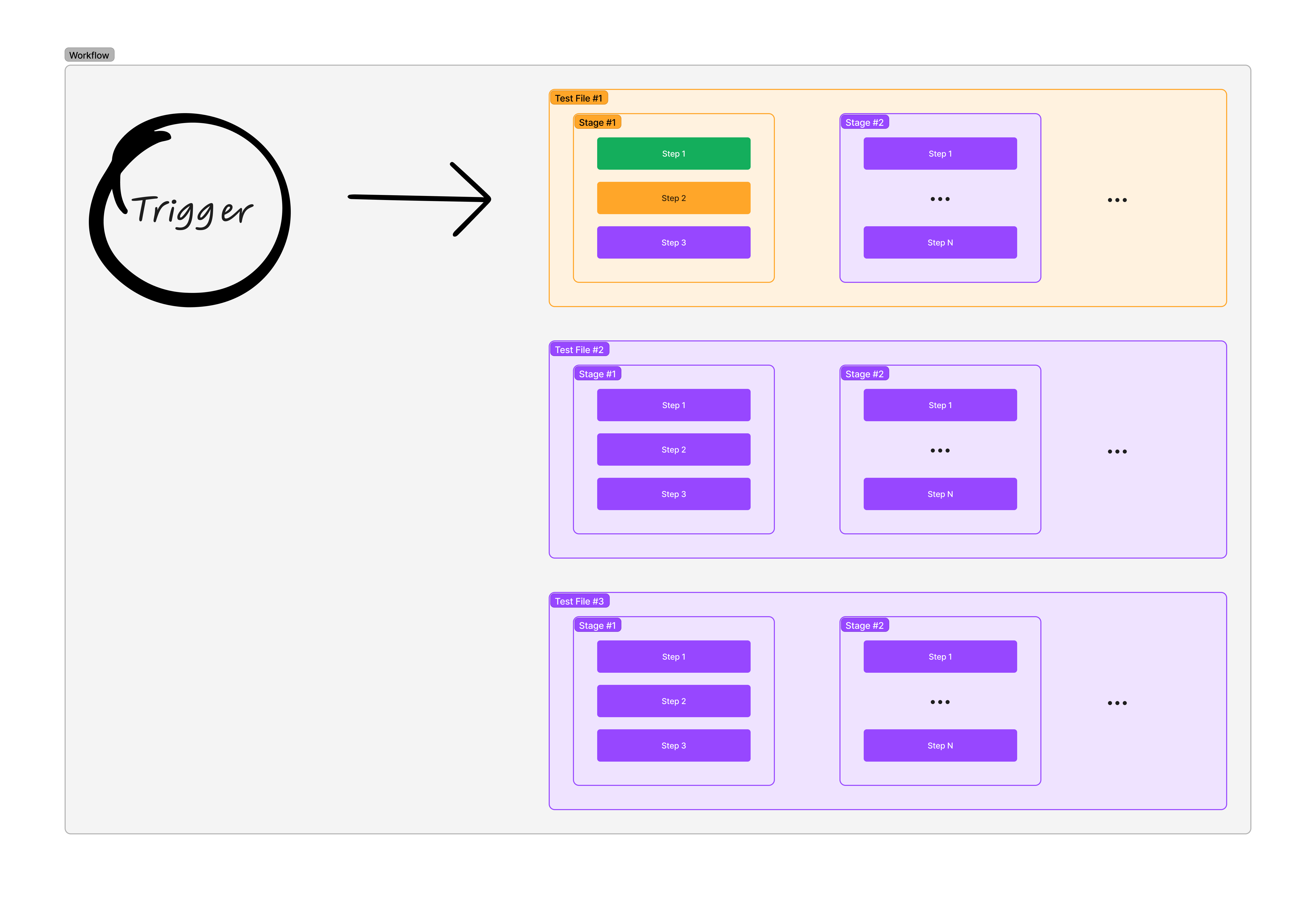
Workflows
Workflows connect all components, defining how tests execute when triggered.
Workflow Components
Hardware Requirements: Defines which DUT labels the workflow targets. Multiple hardware types can be specified.
Test Selection: Lists test files to execute. Tests run sequentially in definition order.
Input Requirements: Declares required inputs like firmware binaries that must be provided when triggering.
Secrets: Stores sensitive data (API tokens, credentials) accessible through template variables.
Execution Flow
- Trigger: Client sends workflow trigger with required inputs (firmware binary, parameters)
- Queue: Server queues the job and reserves appropriate DUTs based on labels
- Preparation: DUTs execute pre-stage operations (flash firmware, configure hardware)
- Testing: Each test file runs sequentially, executing all stages and steps
- Cleanup: DUTs execute post-stage operations and return to the available pool
- Reporting: Server generates reports and notifies the triggering client
Next Steps
- Understand the Test Execution Model for stages and steps
- Learn about Workflow Configuration reference
- Explore DUT Configuration specifications